Did you know? Recent data shows that global demand for sheet metal fabrication equipment is projected to rise by over 5% yearly as manufacturers seek enhanced efficiency and adaptability. In today’s rapidly shifting manufacturing landscape, staying ahead means upgrading to the latest in laser-cutting machines, automated brakes, and precision metal forming tools. Discover how sheet metal fabrication equipment from LVD is not just a necessity for modern factories, but your gateway to increased productivity, cost savings, and smart adaptation in the global trade environment.

Startling Trends: Why Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment is Essential in Modern Manufacturing
“Recent data shows that global demand for sheet metal fabrication equipment is projected to rise by over 5% yearly as manufacturers seek enhanced efficiency and adaptability.”
As manufacturing continues to embrace automation and fast-paced customization, sheet metal fabrication equipment stands out as an essential asset. From automotive plants to aerospace assembly lines, demand for advanced fabrication equipment like metal shears, slip rolls, and sheet metal brakes is surging. Industry-wide, manufacturing leaders recognize that the right metal fab investments can slash production times, elevate product precision, and support reshoring efforts as trade conditions evolve. These tools not only shape and cut materials—often mild steel or high-gauge metals—but also streamline workflows, helping enterprises remain competitive in an era marked by fluctuating tariffs and digital transformation. Choosing the correct fabrication equipment is about more than capacity; it's about future-proofing your operations for a world where efficiency and adaptability dictate success.

What You’ll Learn: Maximizing Value from Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Understand the core features and types of sheet metal fabrication equipment
Explore benefits in efficiency, cost, and precision
Evaluate the latest trends impacting purchasing decisions
Gain insight into top fabrication tools such as metal brakes, slip rolls, and metal shears
By reading this article, you will acquire an actionable understanding of what makes sheet metal fabrication equipment vital for modern manufacturing. Whether you’re an engineer, plant manager, or procurement specialist, you’ll be able to confidently assess the right tools for your workflow—ensuring your operation keeps pace with rapid industry changes. Learn to weigh features like automation, digital integration, and energy efficiency, and see how these choices influence output quality and operational costs. With insights into the pros and cons of common machines—such as metal brakes, slip rolls, and fabrication tools—you’ll leave equipped to make capital investments that offer real, long-term value.
Comprehensive Overview: Types of Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Metal Brakes, Sheet Metal Brakes, and Metal Brakes: Functions and Use Cases
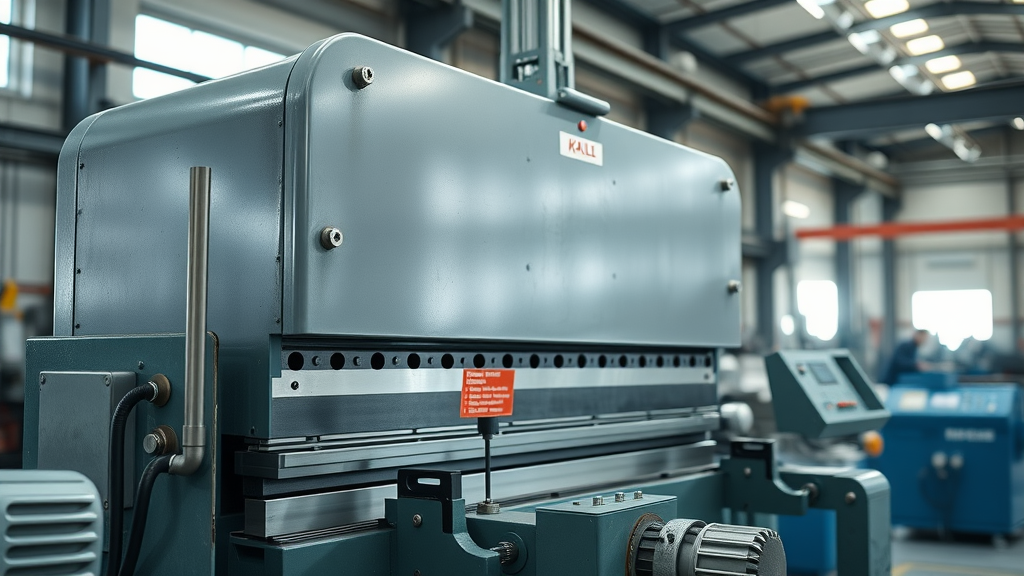

Metal brakes—including box and pan brakes, long folders, and hydraulic models—are foundational to sheet metal bending operations. These machines allow users to form precise bends in mild steel, aluminum, and other metals, ensuring angles and folds meet tight tolerance requirements. Sheet metal brakes are versatile, accommodating a wide range of material thicknesses (gauge mild steel and beyond), and are frequently used in industries like HVAC (for ductwork), automotive, and construction. A box and pan brake is perfect for crafting custom shapes and enclosures, while heavy-duty long folders offer the capacity for lengthy panels used in roofing or vehicle bodywork. For many fabricators, both manual and automated metal brakes unlock productivity, speed, and precision that are otherwise unattainable with hand tools or less specialized equipment.
Key use cases for these brakes include prototyping, small-run production of custom parts, and repetitive commercial tasks. Automation features—such as programmable bending angles and digital control panels—vastly improve cycle times, enabling shops to maintain consistency even across high-mix, low-volume orders. With modern engineering, units from leading brands regularly offer energy-efficient operation and enhanced safety, safeguarding both productivity and employees.
Slip Roll and Metal Shear: Precision Cutting and Shaping Tools
The slip roll and metal shear are indispensable for both the shaping and sectioning of sheet metal. A slip roll allows for the creation of smooth, uniform curves in metals with a range of steel capacity—from thin aluminum sheets to thick gauge mild steel. It’s an essential fabrication tool for producing rolled cylinders, tubes, or curved panels required in a vast array of applications, from auto parts to HVAC systems. On the other hand, the metal shear delivers fast, straight cuts across various metals without the need for saw blades or abrasive wheels—making it a preferred solution for those seeking clean edges and minimal waste.
Shearing machines can handle a spectrum of materials, and today's models come equipped with digital controllers for repeatability and safety guards for operator protection. Slip rolls, available in both manual and powered configurations, streamline the metal forming process and contribute to rapid cycle times in production environments. For shops handling diverse orders, investing in these precision tools minimizes inefficiencies, reduces costs, and guarantees dimensionally-accurate results on every job.
Metal Forming, Fabrication Tool, and Metal Fab Overview
Beyond brakes, rolls, and shears, a modern metal fab shop utilizes an array of fabrication tools for cutting, shaping, punching, and joining metal components. Metal forming machines—such as presses, ironworkers, and benders—expand the range of possible shapes and profiles, especially as product design grows more complex and customized. The integration of advanced fabrication tools with digital controls enables minimal setup times and well-orchestrated workflows, a must-have for facilities working with intricate or high-mix profiles. This holistic approach to metal fabrication consolidates labor, enhances quality, and ensures that even small-batch or prototype work can be performed with industrial-grade consistency and speed.
Keeping up with the growing demand for sheet metal fabrication equipment, manufacturers now seek solutions that fit their exact materials, desired product characteristics, and safety or environmental concerns. The latest metal fabrication equipment maximizes operational flexibility by adapting to both traditional and advanced materials like stainless steel, copper, or composite alloys—making it an asset for both legacy factories and state-of-the-art production lines alike.
Comparison of Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment: Function, Materials, Price Range, Typical Applications |
||||
Equipment Type |
Function |
Material Compatibility |
Approximate Price Range (USD) |
Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Metal Brake |
Bending & forming sheet metal |
Mild steel, stainless, aluminum |
$2,500–$125,000+ |
HVAC ducts, panels, enclosures, prototypes |
Slip Roll |
Rolling curves and cylinders |
Gauge mild steel, aluminum, copper |
$800–$50,000+ |
Tubes, rolled panels, tanks, round components |
Metal Shear |
Precise straight cuts |
Steel, stainless, aluminum |
$2,000–$80,000+ |
Sheet prep, panel sizing, blank production |
Press Brake |
Complex bends & multi-step forming |
Wide range including high-strength steels |
$10,000–$250,000+ |
Chassis, frameworks, brackets, custom job-shop tasks |
Key Features to Look for in Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Automation options and digital integration
Durability and material compatibility
Safety features and operator controls
Energy efficiency

When evaluating sheet metal fabrication equipment, focus on how well each machine supports integration into your existing workflow and future modernization. Automation—from CNC control to programmable operation and digital monitoring—translates to fewer errors, faster job changes, and less downtime. This aids in maintaining consistent product quality even as designs change or global trade conditions shift. Equipment built with durable components is crucial for operations relying on high steel capacity or heavier gauge mild steel, as wear and tear can dramatically affect uptime and long-term ROI.
Advanced fabrication equipment also emphasizes safety, featuring accessible emergency stops, protective guards, and user-friendly operator controls. With increasing energy prices, energy-efficient drives, smart sensors, and sleep modes play a vital role in cutting operational costs. Ensuring material compatibility means your investment will serve across a wide range of metals, including stainless, aluminum, and advanced alloys, allowing you to flexibly pursue new markets and adapt to changes in materials sourcing or product requirements.
The Benefits of Investing in Advanced Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Boosted productivity through rapid cycle times
Accuracy and repeatability in critical operations
Long-term cost savings and reduced waste
Support for reshoring and robust supply chains
Advanced sheet metal fabrication equipment is a direct lever for productivity gains, especially when rapid cycle times are needed for meeting tight deadlines or high order volumes. Integrated automation and programmable metal brakes minimize manual intervention, supporting consistently precise bends and cuts over prolonged runs. For industries where accuracy is critical—such as aerospace or automotive—this combination of precision and repeatability translates to higher product quality and significantly reduced scrap rates.
Perhaps most important for today's manufacturers is the equipment’s role in supporting reshoring and more resilient supply chains. As global trade conditions fluctuate with new tariffs or logistics bottlenecks, companies able to fabricate components in-house stand to maintain business continuity and competitive lead times. Over the lifetime of your machines, reduced waste and error-driven rework mean substantial cost savings and a tangible boost to your facility’s environmental profile.
Industry Applications: Where Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment Shines

Automotive
Aerospace
Construction
Electronics
Industrial Manufacturing
Today, sheet metal fabrication equipment powers production across critical industries. In automotive plants, metal shears and pan brakes create body panels, reinforcement beams, and precision brackets. The aerospace sector, with its uncompromising safety requirements, relies heavily on metal fab equipment for structural skins, engine enclosures, and intricate supports. Construction fabricators turn to slip rolls and long folders for HVAC ductwork, roofing panels, and complex architectural features. High-volume applications in electronics—like chassis or enclosures—demand consistent, repeatable results, making automated fabrication tools a necessity for maintaining throughput and quality. No matter the sector, up-to-date metal fabrication equipment supports better products, shorter production times, and stronger supply resiliency.
Industrial manufacturing covers everything from custom machinery to large-scale production parts. By investing in versatile, adaptable tools, manufacturers can respond quickly to changing market needs or customer specifications, ensuring long-term growth and a reputation for delivering quality every time.
LVD in Action: Navigating Global Trade Challenges with Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
“As an industry leader, LVD has demonstrated how proactive investment in reliable sheet metal fabrication equipment can mitigate risks caused by tariffs and supply chain volatility.”

LVD provides a clear example of how modern manufacturers use investment in sheet metal fabrication equipment to navigate the complexities of global trade. In recent years, shifting tariffs and supply chain uncertainties have pressured businesses to adapt or risk falling behind. By focusing on upgrading their fabrication equipment—integrating automation, robust metal brakes, and digital management systems—LVD has managed to maintain seamless production even as international supply flows change.
This proactive strategy not only insulates the company from sudden logistics disruptions but also fosters the flexibility needed to customize products for diverse markets. For manufacturers seeking to stay ahead during economic headwinds or regulatory changes, LVD’s approach offers actionable insight: investment in durable, efficient equipment strengthens resilience and amplifies the ability to respond to global trends in real time.
People Also Ask: Common Questions About Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
What are the most essential machines in sheet metal fabrication equipment?
The most essential machines in any sheet metal fabrication equipment setup include metal brakes (for bending and forming), slip rolls (for rolling and shaping), and metal shears (for precise, clean cutting). A complete metal fab operation might also use press brakes for complex bends, notching tools, and specialty fabrication tools depending on the product. The exact mix depends on required steel capacity, product range, and industry focus.
How does automation impact sheet metal fabrication equipment efficiency?
Automation drastically enhances the efficiency of sheet metal fabrication equipment by reducing manual steps, lowering error rates, and enabling fast job changeovers. Automated systems, such as CNC metal brakes or integrated material handling, ensure repeatable accuracy and allow facilities to meet higher order volumes without expanding staff. This yields cost savings, shorter turnaround, and greater adaptability in responding to fluctuating demand or design changes.
What should manufacturers consider before investing in new sheet metal fabrication equipment?
Before investing in new sheet metal fabrication equipment, manufacturers should assess material types and thicknesses (such as gauge mild steel capacity and material compatibility), required automation levels, ease of operation, safety features, and support for future digital integration. Life-cycle costs, brand reliability, and alignment with supply chain strategies (like reshoring or international expansion) are also crucial to maximize ROI and ensure manufacturing flexibility.
Real-World Success: Case Studies Using Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Automotive part stamping line: An automotive supplier upgraded to automated metal brakes, reducing cycle time by 30% and cutting material waste through improved precision.
Custom ductwork production for construction: A fabrication shop used programmable slip rolls and shears, allowing them to offer rapid-turnaround HVAC solutions for large commercial projects, enhancing both productivity and client satisfaction.
Aerospace component prototyping: By integrating advanced fabrication tools, an aerospace contractor produced intricate, lightweight enclosures for avionics systems—delivering higher performance with fewer assembly steps and unparalleled consistency.
These real-world cases demonstrate how investing in the right sheet metal fabrication equipment maximizes operational flexibility, decreases time-to-market, and positions manufacturers to outpace competitors—even in industries with strict certification or compliance demands.
Lists: Top Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment for 2025
Automated sheet metal brake systems
High-capacity metal shears
Precision slip rolls
Versatile metal forming machines
Integrated fabrication tool packages
2025’s most in-demand sheet metal fabrication equipment emphasizes automation, multi-material capabilities, and digital control. Buyers are gravitating toward comprehensive fabrication solutions—systems that combine bending, shearing, and rolling tools into one streamlined package. This not only simplifies training and maintenance but also ensures operations can scale with minimal downtime or retooling.
FAQs: Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment for Today's Manufacturer
How is sheet metal fabrication equipment evolving with digital technology?
Digital technology is transforming sheet metal fabrication equipment through smart sensors, cloud-based data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote programming capabilities. Today’s connected machines enable real-time tracking of efficiency, error rates, and maintenance needs, supporting both up-time and quality assurance. Digital integration also provides better traceability—vital for custom orders, compliance, and managing international production standards.
Are there sustainable options in sheet metal fabrication equipment?
Yes, sustainability in sheet metal fabrication equipment is growing, with manufacturers now offering machines designed for low energy use, recyclable materials, and minimal waste. Automated optimization software helps reduce scrap, while energy-efficient drives lower operational costs and environmental impact. Green certifications, eco-friendly coolants, and modular upgrade options further support companies aiming to meet strict environmental standards without sacrificing productivity or product quality.
Key Takeaways: Why Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment Is a Smart Investment
Enhances manufacturing productivity
Supports resilience in volatile global trade climates
Improves product quality, consistency, and precision
Offers long-term ROI via efficiency and automation

Conclusion: Choose Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment for an Edge in Modern Manufacturing
Equipping your facility with top-tier sheet metal fabrication equipment unlocks productivity, optimizes cost, and builds supply chain resilience—giving you a decisive edge in an evolving global marketplace.
Take the Next Step: Stay Ahead of Trade Shifts & Optimize with Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
Manufacturer, don't miss out! Stay informed. Call LVD at 716-542-4511.
Subscribe to Global Trade News for the latest updates. Call 203-271-7991 today.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment