Did you know that in 2023, more than 64% of manufacturers reported significant shifts in their supply chain strategies directly due to rising tariffs? This startling figure highlights just how pervasive the tariff impact on supply chains has become in today's global economy. For manufacturers, importers, and exporters, understanding and overcoming these supply chain disruptions is a matter of necessity—not just competitive edge. In this comprehensive, opinion-driven guide, we’ll break down the facts, reveal industry insights, and equip your organization with the strategies needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving trade environment. Whether you’re struggling with escalating costs, facing new trade barriers, or simply want to future-proof your operations, you’ll find practical solutions and expert perspectives right here.
Tariff Impact on Supply Chains: Uncovering the Facts
Opening Insights: A Surprising Statistic on Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
"In 2023 alone, over 64% of manufacturers reported significant changes in their supply chain strategies directly due to rising tariffs."
Tariffs have transformed from abstract trade policy tools to real-world disruptors of supply chains across the globe. The effects are no longer theoretical; they are driving tangible shifts in the movement of raw materials, finished products, and even the relationships between global trading partners. North American companies are especially impacted as supply chain managers rethink long-standing trade agreements in response to unpredictable trade wars, often sparked by shifts in U.S. trade policy—including actions taken by the Trump administration and subsequent retaliatory tariffs from trading partners like China. As manufacturers scramble to maintain their market share and protect their purchasing power, many are learning firsthand how quickly global supply chains can be thrown into turmoil by sudden changes in tariff rates, import taxes, and trade regulations. Clear, actionable information is more critical than ever for stakeholders in the global supply chain, especially as fluctuating tariffs continually reshape sourcing options, production costs, and ultimately consumer prices.
What You'll Learn About Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
- How tariffs reshape global supply chain relationships
- The three primary effects of tariffs on supply chains and global trade
- Practical solutions for minimizing tariff impact
- Expert opinions on navigating shifting consumer prices and trade wars
Understanding the Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
Defining Tariffs and the Modern Global Supply Chain
At its core, a tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported goods. While the intent might be to protect domestic industries, the tariff impact on supply chains reverberates far beyond mere taxation. Modern global supply chains are intricate webs where a single product might rely on parts sourced from multiple countries, each governed by its own trade policy, free trade agreement, and occasional imposition of import tariffs. The result? When a tariff is levied, the ripple effect can raise costs for raw materials, erode economic activity, and disrupt established flows throughout the global supply chain. With each new round of trade negotiations or escalating trade wars—such as those between the United States and China—logistics hubs, manufacturers, and end consumers all feel the pressure. Today's supply chains demand agility and resilience, especially as frequent policy changes make it harder for businesses to predict operating costs or maintain just-in-time inventories.

Historical Perspective: Tariff Impact on Global Trade and Supply Chain Evolution
Historically, tariffs have served as both economic weapons and bargaining chips in global trade. Trade wars are not a new phenomenon—they echo back centuries, with major disruptions like the Smoot-Hawley Tariff of the 1930s drastically choking international trade and slowing the global economy. In recent years, however, the scale and speed of supply chain evolution have amplified the consequences. The Trump administration’s strategic increase of tariffs on Chinese imports set off a retaliatory cascade: the rest of the world had to quickly reconsider trade agreements, supply sources, and even product design. For manufacturers, such trade wars forced an urgent review of every supply chain node, exposing vulnerabilities that sometimes led to costly sourcing shifts or even complete relocation of manufacturing plants. As global trade continues to evolve, both the history and modern dynamics of tariffs offer essential lessons for how supply chains must respond under pressure.
How Tariffs Affect the Supply Chain: A Closer Look
Supply Chains Under Pressure: How Trade Wars Disrupt Flow
Trade wars place enormous stress on supply chains, upending carefully calibrated logistics and procurement strategies. The imposition of import tariffs on key commodities or finished products means immediate cost increases, frequently leading companies to seek alternative suppliers or reroute shipments to avoid the brunt of tariffs. In North America, for example, tariffs on steel, aluminum, and imported electronics have forced manufacturers to accelerate production cycles, stockpile critical raw materials, or even consider reshoring—returning manufacturing operations back home. The rapid escalation of trade policy disputes often results in congested ports, delayed shipments, and increased operational costs. Such disruptions not only slow down economic activity but reverberate through the global supply chain, impacting everyone from suppliers in China to retailers in the United States and Europe.

Tariffs and Their Role in the Supply Curve
"Tariffs often create a domino effect—raising costs not only for producers but also end consumers through increased consumer prices." – Supply Chain Analyst
When a tariff is applied to imported goods, it effectively shifts the supply curve upward. What does this mean for supply chains? It translates to higher costs at every level—from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to market. The resulting price increases are often passed down the chain, eventually landing on the consumer’s invoice in the form of higher sticker prices. For companies vying for market share, this domino effect threatens both their margins and their ability to remain competitive. Supply chain managers must therefore monitor trade policy developments closely, as a single tariff regulation can alter the financial outlook for entire industries. Ultimately, tariffs disrupt the delicate balance between supply, demand, and price, creating volatility and uncertainty in the global supply chain ecosystem.
Key Effects of Tariffs on Supply Chains and Global Trade
The Three Main Effects of Tariffs: Cost, Operations & Market Shifts
The impact of tariffs can be distilled into three core areas: increased costs, operational complexity, and shifting market dynamics. First, the most direct effect is the increase in production and procurement costs. Tariffs on imported goods, especially critical inputs like steel or electronic components, compel manufacturers to either absorb the higher costs or pass them on to consumers. Second, tariffs often force abrupt operational changes. Companies may need to diversify supplier networks, renegotiate contracts, or resolve compliance challenges, all of which carry inherent risks and delays. Lastly, tariffs create market shifts; as supply chains realign, countries and companies that can produce competitively outside tariff jurisdictions gain advantage, while others lose ground. These effects compound during trade wars, amplifying disruptions across global supply chains and leading to volatile shifts in sourcing, pricing, and international business relationships.
| Region/Market | Cost Increases | Delays | Sourcing Shifts |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 15–25% higher for raw materials | Major port backlogs (weeks to months) | Move to Mexico, Vietnam |
| European Union | 10–18% higher on finished products | Moderate shipping delays | Increased intra-EU sourcing |
| Asia-Pacific | Up to 30% on targeted goods | Disrupted cargo routes | Shift toward ASEAN partners |
Tariff Impact and Volatility in Global Supply Chains
Volatility has become the new normal in global supply chains as tariffs are imposed and repealed with changing political winds. Each new or threatened tariff prompts rapid adaptation—sometimes beneficial, often costly. Businesses that lack diversification or digital supply chain visibility are especially vulnerable. The rise of retaliatory tariffs further complicates matters, triggering unexpected sourcing challenges and even supply shortages. In this environment, agility is essential: companies must adapt to shifting trade policy, accelerating their strategic decision-making and investing in technologies that provide real-time supply chain insights. As the global trade landscape becomes more fragmented, companies able to anticipate and respond to tariff shocks will be those that retain stable market share and avoid the worst of prolonged volatility.
Consumer Prices and the Tariff Impact on Global Supply Chain
How Tariffs Directly Influence Consumer Prices
Few effects of tariffs are as visible as the price tags on the shelves. When tariffs drive up the cost of imported goods or essential industrial components, manufacturers and retailers frequently pass those increases straight to consumers. This results in immediate price increases on everything from consumer electronics and clothing to groceries and cars. The cumulative effect of these increases can strain purchasing power, especially in major economies like the United States, where trade war tensions with China led to observable spikes in consumer prices. Beyond the checkout aisle, this dynamic influences overall economic activity, occasionally sparking inflation and dampening consumer sentiment. Transparency around supply chain disruptions and price changes becomes critical, as informed consumers and buyers increasingly demand accountability from brands and suppliers. The next time you encounter sticker shock, chances are the tariff impact on supply chains played a direct role in making that product more expensive.

"Every new tariff regulation sends ripples across entire supply chains, eventually landing on the consumer's shelf price."
Supply Chain Solutions: Mitigating the Tariff Impact on Global Trade
Reshoring, Diversification, and Smart Sourcing for Supply Chains
Mitigating the tariff impact on supply chains requires manufacturers and logistics professionals to embrace creativity and proactive risk management. One increasingly popular solution is reshoring—bringing production back to domestic or nearby borders to reduce tariff exposure. Meanwhile, supply chain diversification spreads risk by working with multiple suppliers and trade regions, preventing overreliance on a single country or market. Technology also plays a significant role, as investments in digital supply chain management and scenario planning enable more responsive and data-driven decision-making. Practical steps might include mapping vulnerable nodes in your supply chain, negotiating flexible trade agreements, and establishing contingency contracts with second- or third-tier suppliers. Ultimately, those who build adaptability into their supply chain networks earn a distinct advantage amid ongoing trade turbulence.

- Identifying new markets and suppliers: Expand sourcing to regions unaffected by current or threatened tariffs.
- Investing in digital supply chain visibility: Use real-time data and analytics to quickly spot bottlenecks, price changes, or emerging risks.
- Collaborating across global trade regions: Form alliances and partnerships to benefit from free trade areas and shared logistics infrastructure.
- Scenario planning for future trade war disruptions: Prepare playbooks for different tariff scenarios to minimize downtime and financial exposure.
Expert Opinions: Perspectives on Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
"Success in the face of tariff challenges means relentless agility and constant supply chain monitoring." – Global Trade Expert
Experts agree that navigating the modern tariff landscape demands vigilant supply chain monitoring and strategic foresight. Agility is key; organizations that can adapt quickly to changing trade agreements, retaliatory tariffs, or sudden regulatory changes will fare best. Supply chain professionals now function more like risk managers—constantly analyzing global news for the next policy pivot, disruption, or opportunity. By fostering continuous learning, sharing best practices, and investing in supply chain technology, companies can better predict the potential impact of future tariffs and avoid repeating past mistakes. In the long term, those who anticipate change and remain flexible in sourcing, procurement, and logistics will maintain a competitive edge and support more resilient global trade networks.
People Also Ask: Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
How do tariffs affect the supply chain?
Tariffs disrupt supply chains by increasing the cost of imported components, forcing companies to seek new sourcing options and often causing production delays. When tariffs are imposed, companies must quickly decide whether to pass on these costs to consumers, absorb them in their margins, or overhaul their procurement strategies. The result can be longer shipping times, strained supplier relationships, and fluctuating market share—all adding complexity to an already intricate global supply chain.
How does a tariff affect the supply curve?
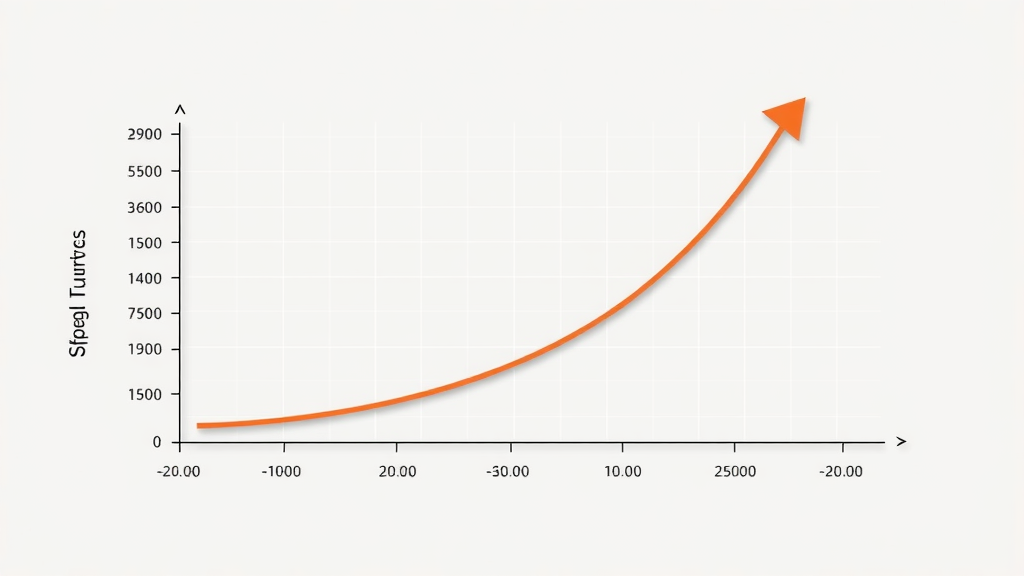
Tariffs shift the supply curve upward, indicating higher costs at each quantity supplied and resulting in reduced supply. This means that for every level of demand, less product is available at a given price—or prices go up to sustain supply levels. This basic economic principle underscores how even modest tariffs can create significant ripple effects throughout global supply chains, affecting everything from raw materials procurement to retail prices.
What are the three main effects of tariffs?
Tariffs typically increase production costs, alter global trade patterns, and lead to higher consumer prices. The initial cost burden falls on manufacturers but ultimately filters down to end-users. As sourcing and trading patterns shift, some companies may gain market share by avoiding highly tariffed goods or markets, while others lose competitiveness due to higher input costs and disrupted relationships with trading partners.
Do tariffs make the stock market go up?
While tariffs can sometimes boost domestic stocks temporarily—especially in protected industries—widespread trade disruptions often create uncertainty and volatility, which usually leads to market declines. Investors warily watch trade negotiations and the potential impact of new tariffs, knowing that prolonged disputes can dampen economic activity and reduce global growth prospects.
A short animated explainer breaking down how tariffs affect sourcing, costs, and consumer prices in global supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions: Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
- How do companies negotiate tariff exemptions? Companies typically work with trade lawyers and government agencies to qualify for exemptions based on product classification, end use, or unique industry needs. Staying informed on trade policy changes improves your chances of securing timely exemptions.
- What strategies help manufacturers adapt to trade tensions? Leading strategies include supply chain diversification, scenario planning, investing in digital procurement tools, and developing strong relationships with multiple global suppliers and logistics partners.
- Are tariffs here to stay in global supply chain planning? While the future of tariffs depends on political and economic developments, most experts recommend planning with the assumption that tariffs will remain a significant consideration in global supply chain management for the foreseeable future.
Key Takeaways: Navigating Tariff Impact on Supply Chains
- Tariffs alter the landscape of supply chain networks globally.
- Diversification and technology are key to supply chain resilience.
- Continuous monitoring helps businesses remain agile amid changing global trade regulations.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Managing Tariff Impact on Supply Chains

In a world of shifting trade policies, resilient supply chains will define tomorrow’s market leaders. Stay agile, diversify, and leverage digital tools for visibility—and you’ll be ready for whatever trade turbulence comes next.
Stay Informed: Next Steps for Manufacturers and Supply Chain Professionals
Manufacturer don't miss out! Stay informed on global trade shifts—tariffs, reshoring, and supply chain updates could reshape your strategy. Subscribe to Global Trade News for Latest updates. Call 203-271-7991 today.
Tariffs have significantly disrupted global supply chains, compelling businesses to adapt swiftly. The article “How Tariffs Are Reshaping Global Supply Chains in 2025” provides an in-depth analysis of how companies are navigating increased logistics costs and shifting sourcing strategies. (supplychainbrain.com) Similarly, “Tariff Impact on Supply Chain: Costs, Risks & Strategy” offers practical solutions for mitigating tariff-related challenges, emphasizing the importance of supplier diversification and strategic planning. (pscs.jabil.com) For those aiming to fortify their supply chains against tariff-induced disruptions, these resources offer valuable insights and actionable strategies.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment